Computer Networks is a digital telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources. In computer networks, computing devices exchange data with each other using connections (data links) between nodes. These data links are established over cable media such as copper wires or fiber-optic cables, and wireless media such as Wi-Fi. Network computer devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Nodes are generally identified by network addresses, and can include hosts such as personal computers, phones, and servers, as well as networking hardware such as routers and switches. Two such devices can be said to be networked together when one device is able to exchange information with the other device, whether or not they have a direct connection to each other.
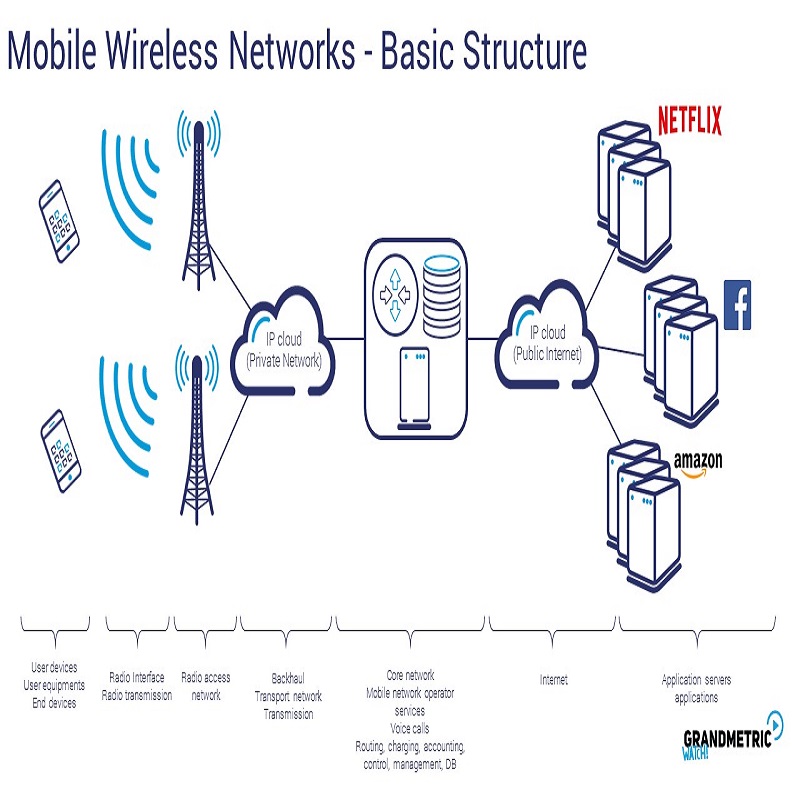
Mobile/Wireless Networks is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and business installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure. Examples of wireless networks include cell phone networks, wireless local area networks (WLANs), wireless sensor networks, satellite communication networks, and terrestrial microwave networks.
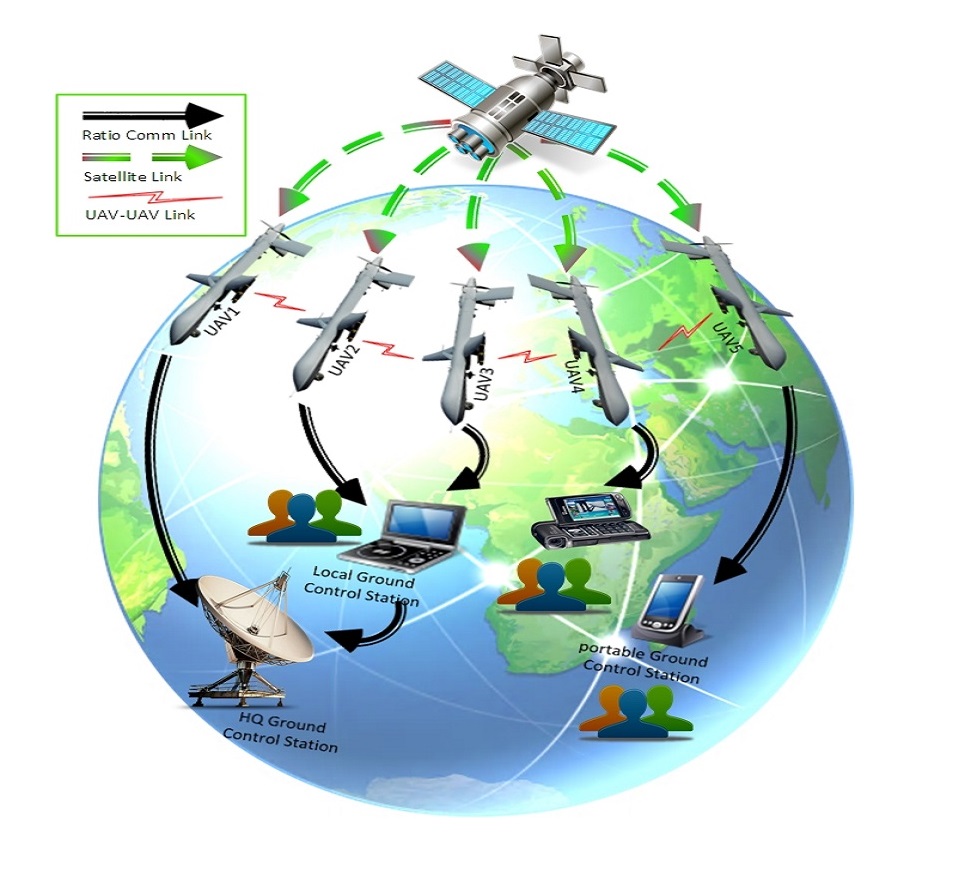
UAV communications are defined as any individual aerial vehicle either in communication with other vehicles, such as a Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) with another UAV (U2U), and a UAV with an Satellite (U2S), or are in communication with stationary infrastructures such as an UAV with Traffic control tower (U2T), and a UAV with Ground station (U2G). A typical scenario for communication among the UAVs is demonstrated in Figure. This scenario includes multiple components and utilizes various links for communication. Each link is responsible for transmitting certain types of data and information. In general, according to type of information being transmitted, there should exist three different types of links in these networks, namely radio communication, U2U and Satellite link.
The internet scope is developed by the Internet of Things (IoT) with the help of physical objects integration in order to categorize themselves to the sharing things. This inventive perception can create a physical object for signifying itself in the digital world. It should be mentioned that about the physical objects, which are linked to the internet, there have been numerous theories and upcoming predictions so that most of them need protected structures, also, are at risk in a large spectrum of attacks. IoTs are in danger of a specific routing disobedience known as physical layer attack due to their distributed characteristic. As a security warning, the physical layer attack makes a condition for the invader to abuse the bandwidth and resources of the network by overloading the
network using insignificant packets.
Blockchain is a public ledger that automatically records and verifies transactions. The distributed ledger technology (DLT) powers Bitcoin, Ethereum and other virtual currencies (which have taken a beating this month). Less publicized are all the ways DLT could transform many industries. Use cases for a transparent, verifiable register of transaction data are numerous because DLT operates through a decentralized platform making it fraud resistant. Once a record has been added to the chain it is very difficult to change. To ensure all the copies of the database are the same, the network makes constant checks. Blockchains have been used to underpin cyber-currencies like bitcoin, but many other possible uses are emerging.